KB full form: Kilobyte
KB Full Form and its Digital Importance
In the intricate landscape of digital data, the units of measurement are like puzzle pieces that fit together to form our technological reality. The acronym KB, a fundamental building block in this landscape, plays a significant role in quantifying the volume of information we generate and share. The full form of KB is “Kilobyte.” In this article, we will delve into the KB full form, grasp its significance in data measurement, and explore how it has shaped the way we understand and manage digital content.
Deciphering the Full Form: Kilobyte
The acronym KB stands for “Kilobyte.” A Kilobyte is a unit of digital information measurement, equivalent to approximately one thousand bytes.
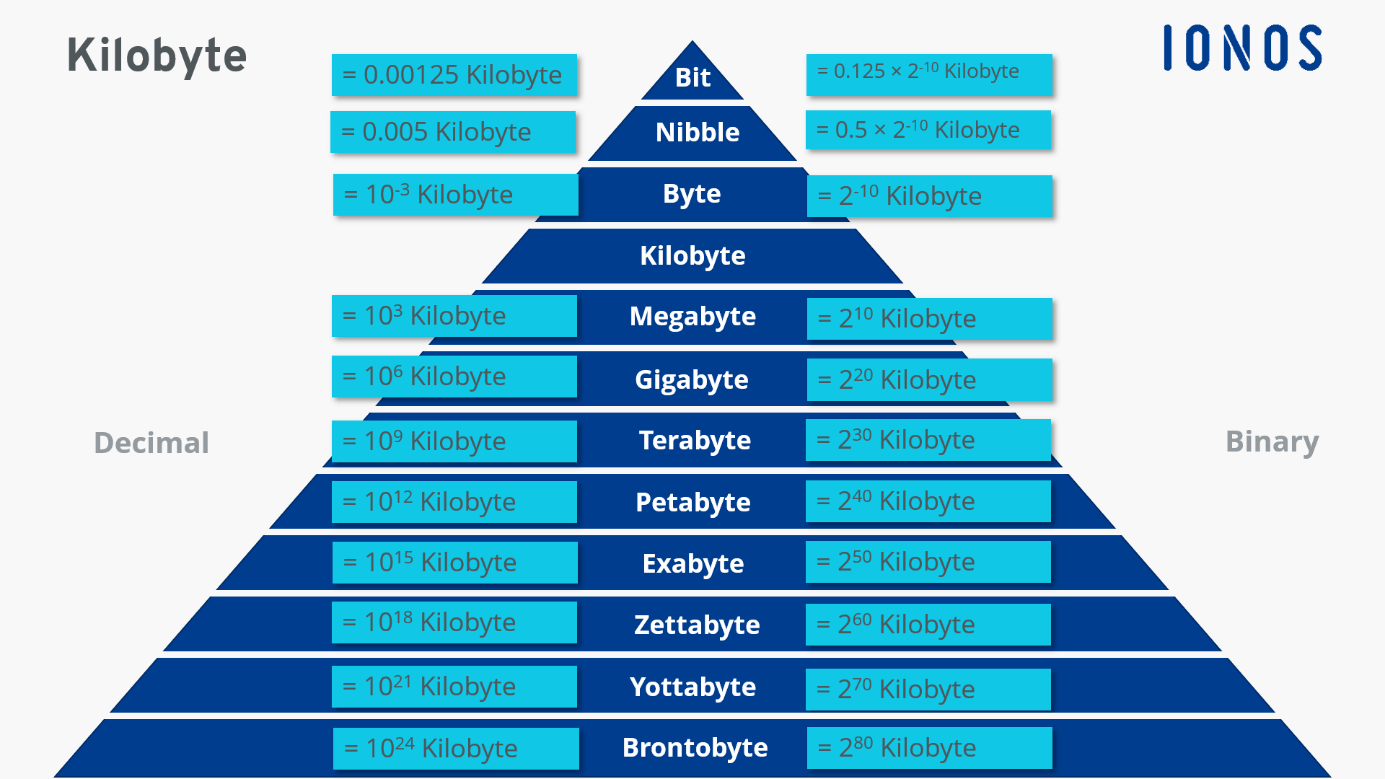
The Evolution of Data Measurement: From Bits to Kilobytes
Understanding the progression of data measurement units helps us appreciate the role of the kilobyte in modern technology:
- Bits: The smallest unit of digital information, consisting of ones and zeros.
- Bytes: A byte comprises 8 bits, forming the basic building blocks for data storage and processing.
- Kilobyte (KB): The kilobyte introduced a higher order of measurement, reflecting the growing complexity of digital information.
Key Features of Kilobytes
- Data Storage: Kilobytes are used to quantify small amounts of data storage, such as text documents, emails, and simple images.
- File Sizes: The sizes of files, documents, images, and small applications are often measured in kilobytes.
- Internet Usage: Early internet connections and data plans were often measured in kilobytes.
Kilobytes in Everyday Context
- Text Documents: Plain text documents and emails typically consume only a few kilobytes of storage.
- Icons and Graphics: Small images, icons, and graphics used in websites and applications are usually measured in kilobytes.
- Early Software: Early computer software and programs were compact and fit within kilobyte-sized memory constraints.
Kilobytes and Technological Advancements
- Rapid Progression: Technological advancements quickly led to larger data storage requirements, rendering kilobytes inadequate for many modern applications.
- Multimedia Content: The rise of multimedia content, high-resolution images, and videos necessitated larger storage units.
Kilobytes vs. Other Storage Units
- Megabyte (MB): 1 MB is approximately 1,000 kilobytes, marking the shift to a larger scale of data measurement.
- Gigabyte (GB): 1 GB equals about 1 million kilobytes, reflecting even greater data storage capacities.
The Future of Kilobytes
- Nostalgic Significance: Kilobytes serve as a reminder of the early days of computing when storage and processing limitations were more prominent.
- Embedded Systems: Kilobytes are still relevant in embedded systems and microcontrollers, where memory constraints persist.
Img source: ionos.com
Conclusion
The KB full form – Kilobyte – embodies a unit of measurement that harkens back to the dawn of digital data. From simple text documents to small images, kilobytes laid the foundation for our digital experiences. As technology continues to evolve and our reliance on digital content deepens, kilobytes stand as a testament to the humble beginnings of the digital era. While larger units of data measurement take center stage in today’s technology landscape, the kilobyte remains a symbol of the digital transformation that has shaped the world we live in today.